#include <Integrator.h>
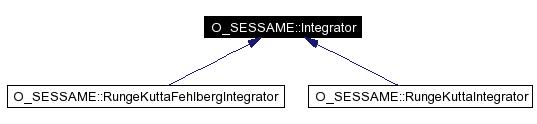
Inheritance diagram for O_SESSAME::Integrator:

This class defines the functions that are required for all Integrator types (ie
AdamsBashfourthIntegrator, etc).
 , where
, where  is the time (in seconds),
is the time (in seconds),  is the vector of states being integrated,
is the vector of states being integrated, 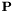 is a matrix of constants, and
is a matrix of constants, and  is a reference to an external function which can be used to evaluate other parameters necessary for the RHS equation. The integration strategy will then evaluate the function
is a reference to an external function which can be used to evaluate other parameters necessary for the RHS equation. The integration strategy will then evaluate the function 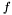 at various timesteps, depending on the integration algorithm, and combine the results together to approximate the integrated solution.
at various timesteps, depending on the integration algorithm, and combine the results together to approximate the integrated solution. :
: 
Definition at line 107 of file Integrator.h.
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual Matrix | Integrate (const vector< ssfTime > &_propTime, odeFunctor _FunctorPtr, const Vector &_initialConditions, Orbit *_pOrbit, Attitude *_pAttitude, const Matrix &_constants, const Functor &_functorPtr)=0 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Interface to the Orbit & Attitude integration function. This function defines just the interface to any of the derived integration strategies. Because it is pure virtual (virtual ... = 0;), it is not actually implemented, but defines a member function that is required to be implemented by all derived classes. Therefore, the user can be assured this integration function will exist for all derived classes.
Implemented in O_SESSAME::RungeKuttaFehlbergIntegrator, and O_SESSAME::RungeKuttaIntegrator. |
 1.3
1.3